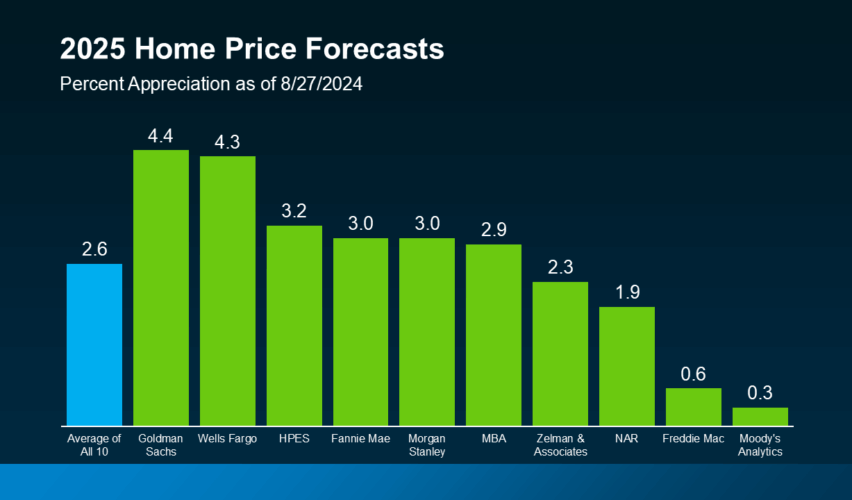
The housing market plays a crucial role in the broader economy, influencing everything from consumer spending to investment strategies. As we move through the current economic cycle, many homeowners, investors, and first-time buyers are asking: what’s next for the housing market?
This housing market forecast will explore key trends, analyze influencing factors, and provide insights into where the market might be headed in the short and long term.
Understanding the Housing Market
The housing market refers to the supply and demand for residential properties, including single-family homes, apartments, townhouses, and condominiums. It is affected by a range of economic, demographic, and political factors that impact housing prices, sales volume, inventory levels, and mortgage rates.
Market conditions can shift quickly in response to interest rate changes, inflation, employment trends, and government policies. Understanding these dynamics is essential for making informed real estate decisions.
Key Factors Influencing the Housing Market
1. Interest Rates and Mortgage Costs
Interest rates, especially those set by central banks, have a significant impact on the affordability of homes. When rates are low, borrowing becomes cheaper, encouraging more home purchases and refinancing. Conversely, rising rates can cool down housing demand by increasing monthly mortgage payments.
2. Inflation and Cost of Living
Higher inflation increases the cost of building materials, labor, and home maintenance. It can also erode purchasing power, affecting what buyers can afford. However, real estate often serves as a hedge against inflation, attracting investors.
3. Employment and Wage Growth
Strong job markets and wage growth support housing demand. When people have stable incomes, they are more likely to qualify for loans and invest in property. Unemployment or economic uncertainty, on the other hand, tends to suppress demand.
4. Housing Supply and Inventory
The balance between available homes and buyer demand directly influences pricing. A shortage of homes typically drives up prices, while a surplus can lead to price corrections. New construction activity also affects this balance.
5. Government Policies and Regulations
Incentives like tax credits for first-time buyers, changes in lending rules, and zoning policies can all influence housing activity. Rent control, property taxes, and development restrictions can also impact both buyer and investor behavior.
Current Trends in the Housing Market
1. Shifting from a Seller’s to a Balanced Market
In recent years, many markets experienced rapid price growth, low inventory, and competitive bidding wars. However, rising interest rates and slowing economic growth have begun to cool the market. Some regions are seeing longer selling times, price reductions, and more negotiation leverage for buyers.
2. Regional Disparities
Housing markets can vary dramatically by location. Urban centers with high demand and limited land often retain higher prices, while rural or suburban areas may offer more affordability. Areas with strong job growth and in-migration—such as tech hubs and southern metros—tend to see more resilience.
3. Demand for Affordable Housing
Affordability remains a major challenge. High home prices and mortgage rates have priced out many potential buyers, increasing demand for smaller homes, condos, or rentals. This has also driven interest in build-to-rent communities and shared living arrangements.
4. Rise of Remote Work and Lifestyle Shifts
Remote and hybrid work models have changed where people want to live. Suburbs, smaller cities, and scenic regions have become more desirable as buyers seek space, quality of life, and value for money.
5. Investor Activity
Institutional and private investors have increasingly entered the housing market, especially in the single-family rental space. While this provides rental inventory, it can also create competition for individual buyers and push up prices.
Short-Term Housing Market Forecast
In the near term, the housing market is expected to remain in a period of adjustment. Key predictions include:
- Moderate Price Corrections: Home prices may stabilize or decrease slightly in overheated markets as demand cools. However, severe declines are unlikely without a significant economic downturn.
- High Mortgage Rates: Interest rates may remain elevated as central banks combat inflation, limiting affordability for many buyers.
- Slower Sales Activity: Fewer transactions are likely as both buyers and sellers take a wait-and-see approach.
- Increased Rental Demand: With homeownership out of reach for some, rental markets will likely see continued strength and possibly rising rents.
Long-Term Outlook for the Housing Market
Over the next five to ten years, several trends will shape the housing market’s trajectory:
1. Gradual Price Recovery and Growth
As interest rates normalize and economic conditions stabilize, housing demand is expected to pick up again, particularly among millennials and Gen Z entering the market. This will support long-term price appreciation, though likely at a more sustainable pace.
2. Urban Revitalization
As cities adapt to post-pandemic realities, investment in infrastructure, public transport, and mixed-use development may make urban living attractive again. This could revitalize demand in downtown areas.
3. Technological Integration
The use of smart home technology, digital closings, virtual tours, and AI in real estate decision-making will continue to expand. PropTech innovations are streamlining the homebuying process and improving efficiency.
4. Green and Sustainable Housing
Demand for energy-efficient and environmentally friendly homes is rising. Builders and developers are increasingly incorporating green building materials, solar panels, and water-saving systems into new construction.
5. Policy and Housing Reform
Governments may implement policies to address affordability issues, such as zoning reforms, rent controls, or subsidies for affordable housing development. These efforts will have a lasting impact on market accessibility.
Opportunities and Challenges Ahead
Opportunities
- Buyers may find better deals as the market cools and competition eases.
- Investors can benefit from growing rental demand and long-term appreciation.
- Builders focusing on affordable and sustainable housing can meet rising demand.
Challenges
- Affordability will remain a barrier for many potential buyers.
- Tight inventory and supply chain issues could delay new construction.
- High borrowing costs may limit mobility and suppress sales volume.
How Buyers and Sellers Can Prepare
For Buyers:
- Get pre-approved for a mortgage to understand your budget.
- Be patient and research local market trends.
- Consider alternative financing options or smaller properties.
- Factor in ongoing costs like property taxes, insurance, and maintenance.
For Sellers:
- Be realistic about pricing based on current conditions.
- Highlight features that align with buyer preferences, such as energy efficiency or flexible space.
- Work with a knowledgeable agent who understands local market dynamics.
- Prepare for longer selling times and potential negotiation on price.
Conclusion
The housing market is entering a new phase marked by normalization and regional variation. While high interest rates and economic uncertainty are slowing activity in the short term, strong demographic demand and a limited supply of housing will likely support long-term growth.
Understanding the trends shaping today’s housing market can help you make smarter decisions—whether you’re buying, selling, or investing. By staying informed and adaptable, you can navigate the evolving real estate landscape with confidence.